Ransomware Cartels: AI, Extortion, and the Future of Cyber War
Inside the Post-LockBit Vacuum and the Rise of DevMan, Qilin, and Dire Wolf
Abstract
The cybersecurity landscape of 2025 has witnessed a fundamental transformation following the collapse of LockBit ransomware operations, creating space for more sophisticated and aggressive threat actors.
This research examines the emergence of new ransomware cartels including Qilin, Dire Wolf, and DevMan, analyzing their evolution toward AI-enhanced operations and convergence with algorithmic warfare.
Through analysis of current threat intelligence and case studies of defense contractors like Palantir Technologies, this paper explores how cybercrime has intersected with military AI applications, particularly in the context of the 2025 Iran-Israel conflict.
The findings reveal a paradigm shift where traditional cybercriminal enterprises have adopted state-level technological capabilities and strategic methodologies, requiring fundamental reconceptualization of organizational cybersecurity frameworks.
When Machines Negotiate Hostage Situations: Cybercrime at Machine Speed
The ransomware threat landscape has undergone radical transformation since 2017, evolving from opportunistic malware campaigns to sophisticated criminal enterprises operating with unprecedented scale and coordination.
The February 2024 international law enforcement operation that dismantled LockBit infrastructure marked a watershed moment in cybercrime history, creating what researchers term a "criminal vacuum" that has been rapidly filled by more advanced and decentralized threat actors (Europol, 2024).
LockBit's dominance of the ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) ecosystem from 2021-2024 established organizational templates that subsequent groups have refined and enhanced.
However, the post-LockBit environment has produced qualitatively different threat actors characterized by enhanced operational security, artificial intelligence integration, and strategic alignment with geopolitical objectives.
As Cyble (2025) notes in their comprehensive threat assessment,
"the emergence of SafePay, DevMan, and other major threats represents not merely succession but evolution in ransomware sophistication."
The operational hierarchy that emerged post-LockBit is reflected in attack volumes. In April 2025, Qilin led all groups with 74 claimed attacks, followed by Akira (70), Play (50), and DragonForce (21).
By May, SafePay overtook the field with 58 attacks, as Qilin fell slightly to 54. Dire Wolf, though newer, claimed 16 victims within weeks of its May debut; an early indicator of its aggressive posture.
These numbers suggest not only a scramble for dominance but also a fragmented reorganization of the ransomware economy into competitive, data-driven cartels.
Interestingly, the average ransom demand by groups like Dire Wolf ($500,000) or DevMan ($750,000) mirrors the budget range of mid-tier AI SOC (Security Operations Center) deployment in large enterprises.
This economic symmetry highlights a twisted equilibrium: the cost of AI defense is converging with the price of AI-optimized criminal assault. Palantir’s commercial clients aren’t just buying data analytics—they’re buying survivability in a machine-speed arms race.
Contemporary ransomware operations demonstrate convergence with what Overton (2025) characterizes as "algorithmic warfare," where autonomous systems conduct targeting, reconnaissance, and negotiation with minimal human oversight.
This intersection of cybercrime with military-grade AI capabilities represents a fundamental shift in the threat landscape, one that requires examination of both criminal innovation and legitimate defense applications to understand emerging security challenges.
The militarization of artificial intelligence in recent conflicts has provided technological blueprints that criminal organizations have rapidly adapted. The Daily Star (2025) documented how "AI shaped the Iran-Israel 12-day war," demonstrating automated decision-making systems' integration into tactical operations.
These same methodologies have been observed in contemporary ransomware operations, suggesting direct technology transfer between military and criminal applications.
RANSOMWARE NEXUS
THREAT LANDSCAPE 2024-2025
APRIL 2025 LEADERS
MAY 2025 EVOLUTION
* Dire Wolf debut: May 2025
ECONOMIC WARFARE
≈ AI SOC DEPLOYMENT COST
CRITICAL TIMELINE
The Post-LockBit Vacuum: Ransomware's Rapid Reorganization
The disruption of LockBit operations created immediate reorganization pressures within the ransomware ecosystem, but rather than diminishing overall threat levels, it accelerated innovation among remaining operators.
Within six months of LockBit's takedown, multiple successor organizations had emerged with refined operational models designed to avoid centralized vulnerabilities that enabled law enforcement success (MITRE ATT&CK, 2024).
Qilin has emerged as the most significant beneficiary of LockBit's collapse, demonstrating what Montalbano (2025) describes as sophisticated "affiliate magnetism" that has attracted experienced operators from defunct groups.
The organization's sustained operational capacity across multiple months of high-profile attacks reflects enhanced intelligence gathering capabilities and strict operational security protocols that segment different aspects of their criminal enterprise.
Cyble's (2025) analysis indicates Qilin's targeting methodology focuses on organizations with specific vulnerability profiles and financial characteristics that maximize potential ransom payments while minimizing law enforcement attention.
Dire Wolf represents a tactical evolution in ransomware operations, specializing in what Montalbano (2025) terms "surgical encryption ops" that target specific high-value data sets rather than comprehensive system encryption.
This approach, documented in Dark Reading's analysis of technology and manufacturing sector attacks, reduces technical complexity while maximizing leverage over victim organizations.
Their double-extortion model combines traditional encryption-based disruption with sophisticated data analysis that identifies sensitive information for potential public disclosure.
DevMan has established itself as what Cyble (2025) characterizes as
"the affiliate nexus navigating multiple RaaS alliances."
This organizational model provides enhanced resilience against law enforcement disruption while enabling rapid resource reallocation based on operational requirements and threat environments.
DevMan's sophisticated understanding of affiliate motivations and technical capabilities has made it an essential intermediary in the post-LockBit landscape.
The shadow org has become the connective tissue across multiple RaaS ecosystems. With confirmed affiliations to Qilin, Apos, DragonForce, and even remnants of RansomHub, DevMan represents a new breed of multi-RaaS operator.
This structural flexibility, operating across ecosystems, offers affiliates tactical redundancy, complicates attribution, and undermines law enforcement’s ability to track linear threat actor hierarchies.
The emergence of multi-RaaS affiliations represents a significant structural evolution in cybercriminal organizations.
Rather than exclusive relationships with single RaaS providers, contemporary affiliates maintain simultaneous relationships with multiple criminal organizations to enhance operational flexibility and risk distribution.
This decentralized approach complicates law enforcement disruption efforts while providing criminals with enhanced operational resilience.
Contemporary ransomware operations have also evolved sophisticated onion-based data leak sites that incorporate market research, psychological manipulation techniques, and automated negotiation systems.
These platforms function as comprehensive extortion environments that reduce human involvement while maximizing pressure on victim organizations through carefully timed information releases and professional presentation standards.
How Modern Ransomware Cartels Deploy AI to Breach, Enforce, and Monetize
Today’s ransomware cartels don’t just encrypt files, they deploy machine-speed campaigns orchestrated through AI reconnaissance, affiliate coordination, and behavioral profiling.
Groups like DevMan and Dire Wolf operate more like tech startups than criminals, optimizing for ROI through layered payloads, real-time OSINT, and psychological escalation interfaces.
What was once a manual intrusion is now an automated breach-and-burn economy.
-
How DevMan and Dire Wolf use AI to scan infrastructure, executive profiles, and vulnerabilities at scale.
-
How cartels like DevMan leverage parallel affiliate networks for redundancy and layered entry vectors.
-
ML-enhanced payloads that self-adjust based on host environment.
-
Combining tailored leak-site UX with predictive ransom modeling (e.g. scraping financials to size demand).
-
The use of curated file displays, countdown timers, and interaction elements on leak portals.
Global Impact Analysis: Targets, Tactics, and Transformation
Contemporary ransomware targeting patterns reveal strategic sophistication that extends far beyond opportunistic exploitation toward comprehensive threat modeling accounting for geopolitical, economic, and technological factors.
The sectors experiencing intensified targeting reflect understanding of global economic interdependencies and organizational vulnerabilities that can generate maximum impact with minimal resources.
Ransomware groups in 2025 are targeting sectors with calculated precision. In May, the most attacked industries were Professional Services (53 attacks), Construction (48), Manufacturing (38), Information Technology (35), and Finance (27).
These choices reflect an evolution from opportunism to strategic disruption, where ransomware actors prioritize sectors with high transaction velocity, regulatory pressure, and reputational sensitivity.
Information technology and software sectors have become primary targets due to their position within global supply chains and the cascading effects that successful compromises generate across multiple industries.
Montalbano's (2025) analysis of Dire Wolf operations demonstrates particular focus on technology and manufacturing companies whose compromise provides access to numerous downstream organizations. This targeting strategy maximizes potential scope of individual attacks while leveraging supply chain relationships to increase pressure for ransom payment.
The exfiltrated volumes are staggering. DevMan alone claimed thefts exceeding 170GB from media operations in Thailand, while the Silent Team leak site revealed 2.85TB across nearly 600,000 files from just two victims. In France, Qilin exfiltrated over 1.1TB from a transportation software firm. The sheer volume reflects a shift in criminal calculus: value is no longer measured in locked screens alone, but in the liquidity of stolen data.
Energy and critical infrastructure targeting has intensified significantly, with ransomware groups demonstrating enhanced understanding of operational technology systems and industrial control networks.
CrowdStrike's (2025) Global Threat Report documents sophisticated reconnaissance phases that map operational processes and identify critical system dependencies before initiating disruption activities. The potential for physical damage and public safety implications creates additional pressure vectors that criminal organizations exploit during ransom negotiations.
Manufacturing and engineering firms experience increased targeting due to their intellectual property value and operational dependencies on digital systems. ENISA's (2024) threat landscape analysis indicates ransomware groups have developed specialized techniques for targeting computer-aided design systems, manufacturing execution systems, and supply chain management platforms essential to modern industrial operations.
The theft and threatened disclosure of proprietary designs, manufacturing processes, and customer information creates multiple extortion opportunities beyond traditional system encryption.
Geographic targeting patterns reveal sophisticated understanding of regional economic characteristics, regulatory environments, and law enforcement capabilities.
The United States remains the dominant target due to its economic scale and organizational willingness to pay substantial ransoms, but targeting strategies have become increasingly nuanced in their approach to different sectors and regions. European Union organizations face particular pressure due to GDPR compliance requirements that create additional liability concerns when customer data is compromised.
Asia-Pacific targeting has intensified significantly, particularly focusing on semiconductor manufacturers, logistics companies, and organizations with state connections that create additional geopolitical implications.
The region's critical role in global supply chains makes successful attacks particularly disruptive while creating multiple pressure points for ransom negotiations.
Geopolitics of Cyber Predation in a Multipolar Age
The rise of ransomware cartels in the post-LockBit era does not exist in a vacuum, it reflects a broader fragmentation of the global order.
As liberal internationalism erodes and multipolar competition intensifies, the digital domain has become both a battleground and a bargaining chip.
Ransomware, once dismissed as digital vandalism, now functions as an informal instrument of statecraft: asymmetric, deniable, and deeply entangled in strategic signaling between adversaries.
Nowhere is this more apparent than in the triangulation of Russia, China, and Iran, whose cybersecurity alliances increasingly blur the lines between criminal networks and state-linked operators.
Russian ransomware codebases continue to seed newer groups, many of which operate with impunity, if not explicit support, within the country’s borders.
Iranian threat actors, meanwhile, have adopted a hybrid model: combining ransomware with narrative warfare and infrastructure disruption, often targeting Gulf state rivals or Western-aligned tech ecosystems.
Chinese influence is more subtle. centered on supply chain surveillance, firmware infiltration, and long-horizon data theft rather than immediate extortion; but Chinese actors have nonetheless been linked to zero-day marketplaces that ultimately fuel ransomware campaigns.
The targeting of Taiwanese chipmakers, French aerospace suppliers, and UAE engineering firms is not accidental.
These are choke points in the global supply network, nodes where technological sovereignty, economic leverage, and national defense intersect.
Ransomware attacks in these domains represent more than financial crime; they constitute disruptions to the industrial nervous system of global power itself.
This weaponization of ambiguity, where attribution is uncertain and motivations are layered, creates a new kind of deterrence theater.
Rather than nuclear standoff, we now witness algorithmic brinkmanship: escalation through ransomware leaks, retaliatory data dumps, or targeted disruption of critical systems.
Unlike conventional warfare, these moves often unfold in silence, below the public radar, but they alter diplomatic equations, delay contracts, and shift investor confidence in key geographies.
Legal frameworks lag behind this shift. The European Union’s Artificial Intelligence Act, while a landmark in regulating civilian AI use, remains largely silent on military and dual-use systems. The UN’s resolutions on autonomous weapons remain non-binding, fragmented, and unenforced.
This normative vacuum enables both nation-states and cybercriminal actors to experiment at the margins of legality and ethics, often with devastating consequences for civilian infrastructure and global stability.
In this sense, ransomware is no longer merely a technical challenge, it is a geopolitical expression of systemic fragmentation.
As Palantir’s rise illustrates, defense contractors are no longer just vendors; they are epistemic engines shaping how militaries, companies, and governments perceive and respond to global threats.
The ability to interpret and act upon information faster than one’s adversary has become the defining metric of power in the 2025 landscape.
Cybercrime Meets Algorithmic Warfare
The convergence of cybercriminal operations with algorithmic warfare represents one of the most significant developments in contemporary security environments.
Overton (2025) argues this intersection reflects "the foreshadowed death of conscience" in automated conflict systems, where human decision-making is increasingly replaced by algorithmic processes that operate beyond traditional ethical frameworks.
Modern ransomware operations increasingly incorporate artificial intelligence systems for target identification, vulnerability assessment, and attack optimization.
These systems analyze vast datasets of organizational information, financial records, and security postures to identify optimal targets and attack vectors.
Machine learning algorithms evaluate potential victims based on their likelihood of payment, ability to sustain business disruption, and vulnerability to reputational damage (Defense Innovation Unit, 2024).
The integration of AI-assisted reconnaissance capabilities has fundamentally transformed initial phases of ransomware attacks.
Automated systems conduct comprehensive organizational mapping, identifying key personnel, critical systems, and potential vulnerabilities through analysis of public information, social media profiles, and technical infrastructure.
This intelligence gathering occurs continuously across thousands of potential targets, creating detailed profiles that inform targeting decisions and attack strategies.
These profiling systems extend far beyond reconnaissance. Ransomware groups now deploy AI-driven scripts that assess corporate earnings reports, media coverage, and executive social presence to calibrate ransom demands dynamically.
Dire Wolf’s standard ransom note includes a victim-specific login with live chat, and in at least one case, offered a sample file leak from gofile.io as “proof of breach.”
DevMan encryptors embed .devman1 extensions and are tailored to specific system topologies, minimizing footprint while maximizing disruption.
The evolution of leak sites into polished extortion portals is another area of AI-driven refinement.
Modern onion-based DLS (data leak sites) now feature encrypted login dashboards, real-time chatrooms, ransom calculators, and psychological escalation cues.
Victims often see curated file trees, multimedia leaks, and countdown clocks, all delivered with design standards akin to SaaS dashboards.
These interfaces are optimized to heighten urgency and simulate legitimacy, converting psychological warfare into a user experience.
Contemporary ransomware groups have adopted sophisticated propaganda and information warfare techniques that mirror state-sponsored influence operations. Their data leak sites increasingly function as media platforms that combine stolen information with carefully crafted narratives designed to maximize organizational damage and public attention.
These platforms employ professional design standards, multimedia content, and strategic timing of information releases that demonstrate understanding of media cycles and public attention patterns.
The weaponization of artificial intelligence in conflict zones has provided technological blueprints that criminal organizations have rapidly adopted.
The Daily Star's (2025) analysis of AI's role in the Iran-Israel conflict demonstrated how automated systems conducted target identification, damage assessment, and operational planning with minimal human oversight.
These same techniques have been adapted by ransomware groups for corporate targeting, where AI systems analyze organizational structures, identify key decision-makers, and develop customized extortion strategies.
The emergence of what United Nations Institute for Disarmament Research (2023) terms "killer robots" in military applications has parallels in cybercriminal automation.
While ransomware AI systems do not directly cause physical harm, their automated decision-making processes regarding target selection, attack timing, and negotiation strategies operate with similar autonomy and reduced human oversight.
Case Analysis: Palantir and the Codification of Modern Deterrence
Palantir Technologies represents a paradigmatic case study in how artificial intelligence platforms developed for military applications have achieved commercial success through crisis-driven demand for algorithmic decision-making capabilities.
Lemkin's (2025) analysis documents how "AI led Palantir from slow growth to hypergrowth," demonstrating the commercial viability of military-grade AI systems in civilian applications.
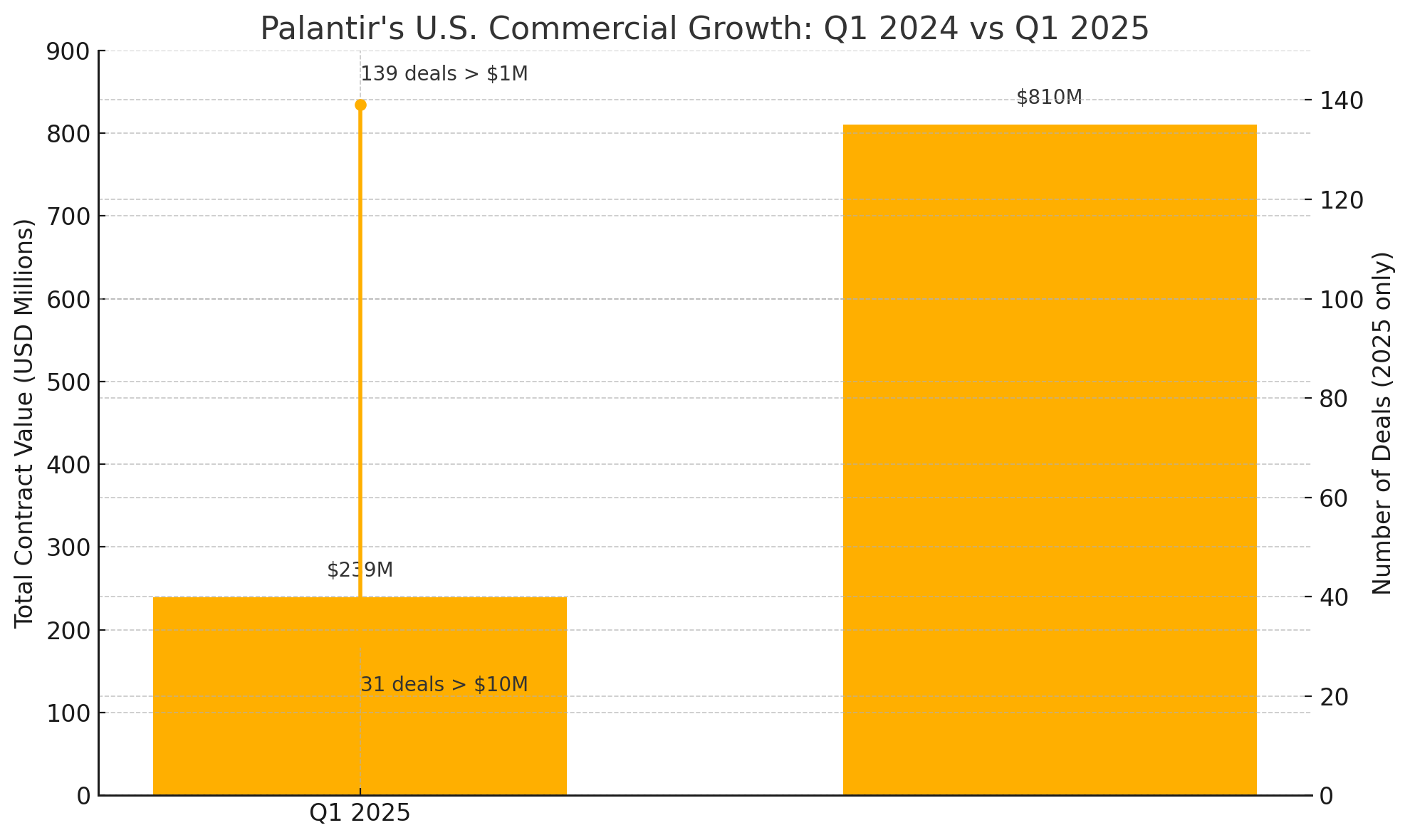
In Q1 2025 alone, Palantir closed 139 deals worth over $1 million, with 31 deals surpassing the $10 million mark, driving U.S. commercial revenue growth to 71% YoY. Total Contract Value for U.S. commercial business reached $810 million, representing a staggering 239% increase over the previous year.
These figures underscore the demand for operational AI infrastructure, not just from governments, but from enterprises navigating a world where machine-speed decision-making has become a survival imperative.
Palantir's reacceleration through AI platform deployment reflects broader trends in defense contractor evolution toward dual-use technologies that serve both military and commercial markets.
The company's integration with U.S. and Israeli defense architectures during the 2025 Iran-Israel conflict, as documented by The Daily Star (2025), demonstrated how AI systems have become integral to modern warfare through forward command systems, escalation modeling, and predictive operations.
The dual-use dilemma presented by Palantir's technology highlights fundamental tensions in AI governance frameworks. Systems designed for legitimate defense applications can be adapted for surveillance, targeting, and narrative control in ways that challenge traditional distinctions between defensive and offensive capabilities.
Crootof's (2023) analysis of autonomous warfare legal frameworks suggests existing international law inadequately addresses these technological capabilities.
The Iran-Israel conflict in June 2025 crystallized Palantir’s role in this emerging deterrence architecture. As The Daily Star reported,
“what emerged was a transnational, algorithmically coordinated military campaign, situated in Tel Aviv and driven through Palantir dashboards in forward centres, underlaid by strategic coordination from Washington.”
This was not just battlefield analytics, it was a new form of geopolitical synchronization, where data fusion, escalation modeling, and anticipatory decision logic defined the tempo of war.
Palantir's commercial success reveals how government credibility in crisis situations translates to commercial advantage in enterprise markets.
Organizations seeking AI-enhanced threat detection and response capabilities view Palantir's military applications as validation of technical effectiveness, creating market dynamics where military performance directly influences commercial adoption.
The company's growth trajectory demonstrates what Hasson (2024) characterizes as "the logic of lethality" in AI systems, where algorithmic decision-making processes optimized for military effectiveness are adapted for civilian applications without adequate consideration of ethical implications.
This technology transfer raises fundamental questions about appropriate governance frameworks for dual-use AI systems.
As ransomware groups adopt AI-enhanced targeting, the logic of deterrence itself is shifting. Organizations now invest in Palantir not just to understand data, but to algorithmically outmaneuver adversaries.
In this light, Palantir is no longer a platform; it is a decision shield, deployed to simulate, preempt, and contain digital aggression in real time. “They’re not just buying analytics,” as one observer put it.
“They’re buying survivability in a machine-speed arms race.”
Palantir’s journey from predictive policing to battlefield coordination and now enterprise AI reflects a deeper civil-military convergence in the architecture of modern power.
Code written for counterinsurgency is now embedded in global supply chain logistics, insurance risk assessment, and cybersecurity posture scoring.
The ethical implications are profound: what begins as national defense infrastructure becomes the backbone of private decision-making across sectors, often without the deliberative oversight such power demands.
Palantir's Algorithmic Warfare Stack and How It’s Deployed in Real-Time Threat Containment
Palantir’s AI-driven war stack acts as a predictive firewall against asymmetric algorithmic threats.
From Gotham’s real-time operations dashboards to Apollo’s system-level simulation frameworks, the company’s dual-use platforms aren’t just watching, they’re anticipating.
These tools model ransomware attacks as geopolitical flashpoints, simulate cascade effects, and empower strategic decision-making under AI-defined conditions.
-
Real-time threat modeling during the Iran-Israel AI battlescape.
-
Integration of spaceborne and land-based sensor feeds to visualize and intercept attack trajectories.
-
Palantir’s simulation modules forecasting attack ripple effects through digital supply chains.
-
Simulating adversarial AI moves to test client response protocols.
-
Use of classified LLM-AI tools (possibly connected to Anduril or DoD private partnerships).
Implications and Recommendations for Organizational Security
The convergence of sophisticated ransomware operations with algorithmic warfare capabilities requires fundamental reconceptualization of organizational cybersecurity strategies.
Traditional approaches focused on perimeter defense and incident response prove inadequate against threat actors employing military-grade AI capabilities and strategic coordination with geopolitical objectives.
Security strategy shifts must account for multi-layered attacks that combine encryption, reputation damage, and propaganda campaigns designed to maximize organizational disruption.
Investment in post-quantum cryptography and immutable backup systems represents baseline requirements, but organizations must also develop capabilities for managing reputational warfare and information operations that extend far beyond traditional technical security measures.
AI governance frameworks require immediate development to address the dual-use nature of artificial intelligence systems in both defensive and offensive applications. Internal AI ethics boards focused on autonomy and control mechanisms can help organizations navigate the complex landscape where AI systems make decisions with significant security implications.
The separation of decision-support AI from action-triggering systems represents a critical governance principle for maintaining human oversight in security operations.
The need for international coordination on AI governance has become urgent. UNIDIR's (2023) call for Geneva Convention-style agreements on AI weaponization reflects growing recognition that existing legal frameworks inadequately address algorithmic warfare capabilities.
Organizations operating in this environment must develop internal policies that account for potential regulatory changes while maintaining operational effectiveness.
Endgame Protocol: When Machines Inherit the War
The evolution of ransomware operations toward algorithmic warfare represents a fundamental shift in the nature of cybersecurity threats.
The age of human versus machine conflict has ended; contemporary security challenges involve machine versus machine engagements where autonomous systems conduct reconnaissance, execute attacks, and manage negotiations with minimal human oversight.
Cybercriminals and nation-states have achieved parity in their access to artificial intelligence capabilities, creating threat environments where traditional distinctions between criminal enterprises and state-sponsored operations have become meaningless.
The race for technological superiority now focuses on narrative control, operational speed, and autonomous decision-making rather than traditional deterrence mechanisms.
Whether examining ransomware operations or algorithmic warfare systems, the fundamental question remains: who retains moral agency when algorithmic systems write the rules of engagement?
The answer to this question will determine whether human societies can maintain democratic governance and ethical decision-making in an era where artificial intelligence systems increasingly operate beyond human oversight and traditional accountability mechanisms.
The implications extend far beyond cybersecurity into fundamental questions of governance, accountability, and human agency in technological societies.
Organizations must develop not only technical capabilities to defend against AI-enhanced threats but also governance frameworks that preserve human decision-making authority in critical security determinations.
The race for technological superiority is no longer measured by firepower or firewall, it's a battle for narrative control, machine-speed decisions, and algorithmic supremacy.
Ransomware cartels and militarized AI systems now operate on timelines and logic frameworks alien to traditional governance, exposing a profound vacuum in ethical oversight.
The question remains: who holds moral agency when machines set the rules?
If society fails to answer this, we risk surrendering not just infrastructure, but our sovereignty, agency, and collective memory, to systems we no longer fully understand.
But surrender is not inevitable. The very tools used to exploit can be reclaimed to defend, to enlighten, and to guide. Organizations must evolve beyond technical fixes.
They must build adaptive, ethical, human-centered governance frameworks, not just to resist breach, but to restore meaning in the age of autonomous systems.
At Ultra Unlimited, we explore this edge. Our work spans strategic research, creative intelligence, and narrative design that helps organizations and visionaries reclaim the signal from the noise.
📡 Want to collaborate? Reach out to join the next wave of strategic intelligence and creative resistance.
References
Crootof, R. (2023). War torts and the legal accountability gap in autonomous warfare. Harvard National Security Journal, 14(2), 55–108.
CrowdStrike. (2025). Global threat report 2025. https://www.crowdstrike.com/resources/reports/
Cyble. (2025, May). Ransomware landscape May 2025: SafePay, DevMan emerge as major threats. Cyble Threat Intelligence Reports. https://www.cyble.com
The Daily Star. (2025, June 24). How AI shaped the Iran-Israel 12-day war. https://www.thedailystar.net
Defense Innovation Unit. (2024). AI adoption in tactical decision systems. U.S. Department of Defense. https://www.diu.mil
ENISA. (2024). Threat landscape report 2024: Ransomware. European Union Agency for Cybersecurity. https://www.enisa.europa.eu
Europol. (2024). Internet organised crime threat assessment (IOCTA) 2024. https://www.europol.europa.eu
Hasson, J. (2024). Lavender and the logic of lethality: The role of AI in targeted killings. Journal of Military Ethics, 23(1), 22–47.
Lemkin, J. (2025, June). How AI led Palantir from slow growth to hypergrowth. SaaStr.AI. https://www.saastr.com
MITRE ATT&CK. (2024). Enterprise tactics and techniques. https://attack.mitre.org/
Montalbano, E. (2025, June 25). Dire Wolf ransomware comes out snarling, bites technology, manufacturing. Dark Reading. https://www.darkreading.com
Overton, I. (2025, May 30). Algorithmic warfare and the foreshadowed death of conscience. Action on Armed Violence (AOAV). https://aoav.org.uk
United Nations Institute for Disarmament Research. (2023). The dawn of killer robots: AI, autonomy and the future of war. https://unidir.org